Title:
Synthesis of bio-derived high-performance polybenzimidazoles from an exotic amino acid 3-amino-4-hydroxybenzoic acid
Speaker(s):
Aniruddha NAG1, 2, Mohammad Asif ALI1, 3, Seiji TATEYAMA1, Tatsuo KANEKO1, 3
1School of Materials Science, Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Ishikawa 923-1211, Japan
2M. Tech (CSPT), Department of Chemistry, University of Delhi, Delhi 110007, India
3JST, CREST
Phone: +81-761-51-1633, Fax: +81-761-51-1635, E-mail: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Abstract:
Development of bio-based plastic is important for establishment of green-sustainable society. Aliphatic polyesters such as poly-(lactic acid) are successful examples, but have low thermo-mechanical properties, and their applications are limited. To broaden the application of bio-plastics, we develop bio-plastic with high thermo-mechanical performance similar to engineering plastics by utilizing renewable 3-amino-4-hydroxybenzoic acid (3, 4-AHBA) which can be derived from antinomycetes metabolite. Our designed bio-based polybenzimidazole (PBI) is expected to show stronger and better heat resistance compared to polybenzazoles, because PBI contains some special structural characteristics like-rigid cyclic structure, π-π stacking interaction, axial symmetry and hydrogen bonding between N-H bonds and they are light weighed, high mechanical strength engineering scale plastics.
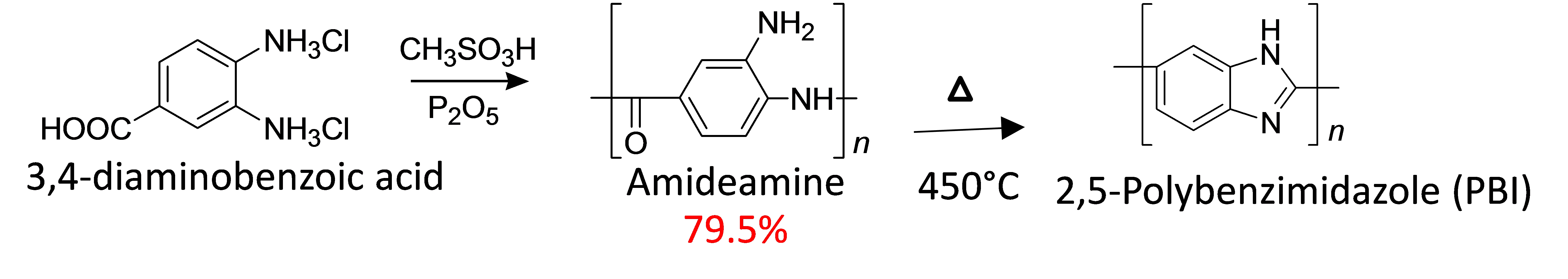
Scheme: 1. Synthetic pathway of the homopolymer 2, 5-polybenzimidazole (2, 5-PBI)
However, PBI has never been synthesized from renewable resources because the aromatic diamine or tetraamine which are monomers of PBI, have high toxicity for organisms. Here we focused on synthesis of bio-based PBI using diaminobenzoic acid (monomer) from bio-derived 3, 4-AHBA by stepwise chemical reactions. It includes a key reaction of Smiles rearrangement which involves conversion of hydroxyl to amine group. After this bio-based monomer 3, 4-DABA has been synthesized we have tried to make the homopolymer 2,5-polybenzimidazole (PBI) and copolymer polybenzimidazole-benzamide were synthesized and characterized in various ways to check its thermal and mechanical strength. Thermal reaction was characterized by TGA machine and we tried to change the amideamine to imidazole group by heating at around 400-450°C.
In both the cases structure has been confirmed by FT-IR spectra as the polymers were unable to dissolve in any kind of solvents except acids. The crystalline behavior of homopolyner and copolymer PBI were investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD) in between 40-60%. T10(10% decomposition temperature) recorded by TGA of 2, 5- PBI and polybenzimidazole-benzamide was in between 625-675 °C and mechanical properties are also comparable to engineering plastics.
[REFERENCES]
1. Kim H., et al, Macromol. Rapid Commun. 25, 894-897 (2004).
2. Kaneko, T., Thi, T. H., Shi, D. J. & Akashi, M. Nat. Mater., 5, 966-970 (2006).